4C/ID MODEL:
In the article Blueprints for Complex Learning: The 4C/ID-Model, van Merrienboer, Clark, and Croock (2002) offer an explanation of an instructional design model entitled the 4C/ID-Model. The model is based on 4 main components. When these components are considered an effective learning structure can be created that will allow for training in complex learning situations.
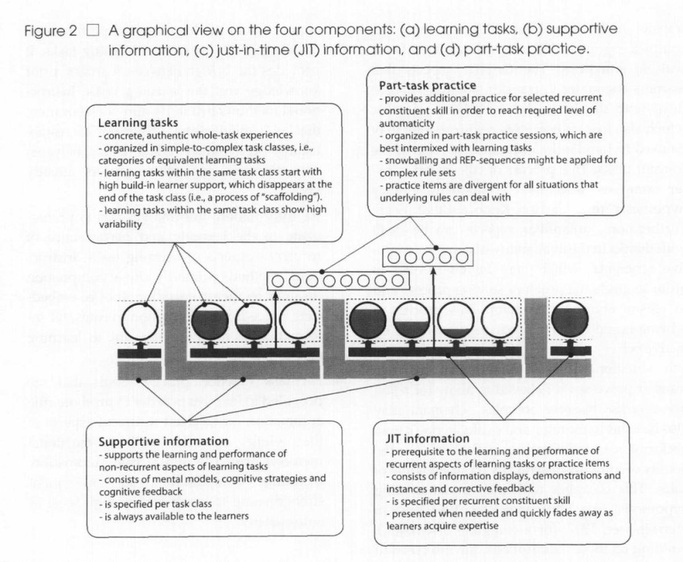
These components are (1) learning tasks, (2) supportive information, (3) just-in-time (JIT) information, and (4) part-task practice (van Merrienboer et. al., 2002).
The learning tasks themselves are the most important component of the 4C/ID-Model. Learning tasks include group projects, case studies, or simulations that require the learner to use or construct new knowledge. The authors of the article also come to this conclusion by stating: "A sequence of learning tasks is the backbone of every training program aimed at complex learning (van Merrienboer et. al., 2002). Learning tasks confront the learners with all the constituent skills that make up the whole complex skill (van Merrienboer et. al., 2002).
The other 3 components of the design model act as support for the learning tasks. Supportive information is provided to allow the trainee or learner the opportunity to obtain the needed knowledge and theories to complete the learning tasks. Examples of supportive information would include videos, books, or articles. Just-in-time information is provided to scaffold the learner through the learning task. Examples of just-in-time information would include instructions, manuals, or pop up support within a computer
program. Finally, part-task practice is conducted to ensure complete competence with the complex skill and to give the learners the ability to apply the knowledge and skills to the learning tasks quickly. Examples of part-tasks practice would include repetitive training exercises such as a child memorizing multiplication tables that ensure quick recognition and use of the skills taught.
Supportive information is almost as important a component of the 4C/ID-Model as the learning tasks. Once the learning tasks are confirmed supportive information is needed to supply a pathway which bridges the learner from their current level of understanding to the new content that is being presented.